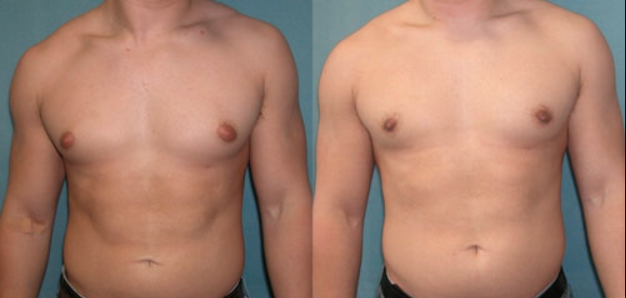
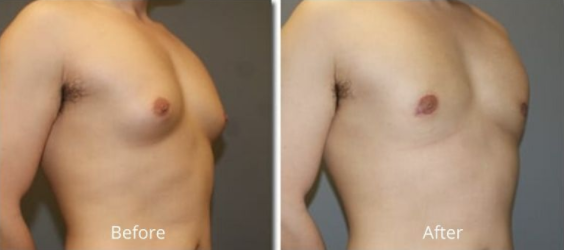
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia, also known as the enlargement of the male breast, is a common condition in which the amount of breast gland tissue in boys or men has excessively increased. Male breast enlargement is mostly caused by an imbalance between male and female hormones – testosterone and estrogen.
Gynecomastia occurs typically in both breasts, but sometimes it can affect either one unevenly. As a result of the gynecomastia condition, male breasts may resemble female breasts.
Can This Happen to Me?
The enlargement of the glandular tissue of the male breast can happen in different life stages:
- After birth – since fetuses receive estrogen from their mothers while still developing in the womb, more than half of newborn boys are born with enlarged breasts. However, this usually fades away within two or three weeks after birth.
- At puberty – caused by intense changes in hormone levels (typically 12 to 14 years of age), the gynecomastia usually clears out six months to two years after the puberty started.
- At mid-life and beyond – breast enlargement can strike men between the ages of 50 and 80. However, only one in four men in this age range might experience it.
Signs and Symptoms
Since gynecomastia is the enlargement of glandular tissue, the main sign is enlarged breasts, whether it’s both breasts or one of them. However, it’s essential not to confuse gynecomastia with pseudogynecomastia – the latter isn’t the enlargement of glandular tissue, but rather fatty tissue. Pseudogynecomastia, often called “man boobs,” is more related to obesity and an unhealthy lifestyle.
Other symptoms of gynecomastia include swollen breast tissue and breast tenderness. Although tenderness and sensitivity may occur, there is typically no severe pain.
Causes of Gynecomastia
As said before, gynecomastia is mainly caused by an imbalance between the sex hormones testosterone (controls male traits, i.e., body hair and muscle mass) and estrogen (controls female traits, i.e., breast growth). Both men and women produce the opposite sex hormones in small quantities. Still, when estrogen levels in males rise too high or are out of balance with testosterone levels, gynecomastia can be developed.
In addition to the imbalance of sex hormones, there are multiple other health conditions and external factors that can trigger the male breast’s enlargement:
-
- Natural hormone changes – in different life stages, infants, teenagers, and adults may experience gynecomastia (see the second subparagraph).
- Health conditions:
-
-
- Obesity
- Kidney failure
- Liver failure and cirrhosis
- Tumors in the testicles or adrenal glands
- Malnutrition and starvation
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypogonadism
-
- “Street” drugs and alcohol:
-
-
- Amphetamines (used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder)
- Marijuana
- Heroin
- Methadone (Methadose, Dolophine)
- Alcohol
-
- Medications:
-
- Antibiotics
- Anti-androgens (i.e., flutamide, finasteride (Proscar, Propecia), and spironolactone (Aldactone, Carospir))
- Anabolic steroids and androgens
- AIDS medications
- Anti-anxiety medications, such as diazepam (Valium)
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Herbals (e.g., dong quai, tea tree oil, lavender)
- Ulcer medications, such as the over-the-counter drug cimetidine (Tagamet HB)
- Cancer treatment
- Heart medications, such as digoxin (Lanoxin) and calcium channel blockers
- Stomach-emptying medications, such as metoclopramide (Reglan)
Best Treatment for Gynecomastia
Even though gynecomastia mostly disappears over time without treatment, in some cases, it may need treatment, especially if it doesn’t resolve on its own or enlarged breasts are causing significant tenderness, pain, or embarrassment.
If treatment is necessary, it’s reasonable to start with the elimination or addition of some medications in your nutrition. However, if diet adjustments don’t bring the desired results, most of the men opt for gynecomastia surgery, also known as male breast reduction.
Gynecomastia surgery reduces breast size, also flattens and enhances the chest contours. The procedure usually takes 1-2 hours and is performed under general anesthesia. During the operation, the excess mammary gland tissue and surplus fat and skin are removed through an incision made along the nipple’s edge or through it. Depending on the condition, gynecomastia surgery is done separately or simultaneously with fat aspiration.
Essential details about gynecomastia surgery:
- Surgery duration: 1-2 hours
- Anesthesia: general
- Hospital stay: 1 night
- Recovery time: 4-6 weeks
- Work leave required: 1 week
Results and Recovery
Even though the gynecomastia procedure’s final results may take 3-6 months to achieve, the first results are visible immediately. Most patients are delighted with it and genuinely enjoy their new look, even though post-surgical swelling and incision lines take time to tone down.
Most of the time, the patient is allowed to go home the next morning after the surgery. If the procedure consisted only of liposuction to correct the patient’s enlarged male breasts, they could return to mild exercise and work less than a week typically. However, for patients who had surgical removal of the excess breast gland tissue, it can take two weeks up to a month to recover enough to put up with everyday activities.
Also, to help your chest heal optimally, bandages and compression corset need to be worn, up to 2 and 4-6 weeks.
Risks and Complications
Even though the gynecomastia surgery is very safe, and most patients have smooth and easy recoveries, some complications may occur. During the first few days after the operation, mild pain, and a stinging feeling in the wound area are expected. These kinds of complications can be easily alleviated with the help of remedies.
Other complications a patient might experience are visible scars, numbness of the nipples, bruising, bleeding, contour irregularities, loss of nipple skin, fluid collections, inverted nipples, and asymmetries. For the best possible results and to avoid the complications mentioned above, it’s essential to pay attention to pre- and postoperative treatment and be always in touch with your doctor.
Are the Surgery Results Permanent?
Gynecomastia surgery results are permanent, but it’s crucial to stick to a healthy lifestyle, nonetheless. A significant weight gain, certain medical conditions, or the usage of steroids or drugs that affect testosterone levels could evoke gynecomastia’s reoccurrence. In that case, the correction of the gland tissue can be repeated.
All in all, if you are experiencing gynecomastia right now and want to get rid of it to feel more confident in your body, gynecomastia surgery could be the right solution and shortcut to get the chest you deserve!